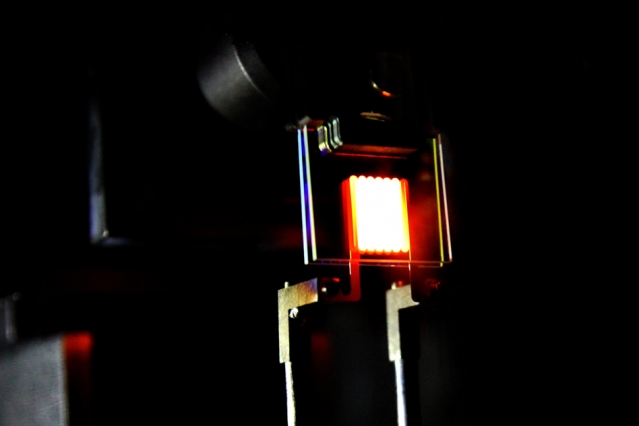
At MIT, researchers found that pulsing lights at 40 cycles per second at mice that are genetically engineered to develop alzheimer’s have a significant reduction in the beta amaloyd plaque that develops in their brain as well as having the right kind of cells stimulated that clean out this plaque.
This video covers the entire concept in a nutshell:
Here are a few excerpts from the article by MIT:
“After an hour of stimulation at 40 hertz, the researchers found a 40 to 50 percent reduction in the levels of beta amyloid proteins in the hippocampus.”
“Using this device, the researchers found that an hour of exposure to light flickering at 40 hertz enhanced gamma oscillations and reduced beta amyloid levels by half in the visual cortex of mice in the very early stages of Alzheimer’s. However, the proteins returned to their original levels within 24 hours.
The researchers then investigated whether a longer course of treatment could reduce amyloid plaques in mice with more advanced accumulation of amyloid plaques. After treating the mice for an hour a day for seven days, both plaques and free-floating amyloid were markedly reduced. The researchers are now trying to determine how long these effects last.”
“Tsai’s lab is now studying whether light can drive gamma oscillations in brain regions beyond the visual cortex, and preliminary data suggest that this is possible.”
Having 20 years experience with pulsed LED technologies and 25 years experience with brainwave modification techniques, light can indeed stimulate gamma wave activity in the brain beyond the visual cortex.
A mentor of mine had a IBVA (Interactive Brainwave Visual Analyzer) back in its early development and it could show brainwave activity visually on a laptop – this was almost 20 years ago. We did many experiments as many unusual human mind power feasts were accompanied by bursts of gamma wave activity in the brain.
Gamma wave have been known about for almost a century and stimulation of the brain with both sound and light in the gamma wave range has shown to reduce migraines, improve concentration, boost math scores and many other academic abilities in multiple areas.
These researchers at MIT appear to simply be pulsing a strip of white LED’s. To reduce the chances of damaging the eyes, it may be preferable to use a mix of red and infrared LEDs in the 660nm and 880nm range. Also, they could stimulate gamma waves in the brain pulsing the lights at one frequency in one eye and a frequency that is different in the other eye.
For example, if red light was pulsed in the right eye at 60 cycles per second and the left eye at 100 cycles per second, the corpus callosum (traffic director between both sides of the brain) will interpret a phantom frequency of the difference between them. Therefore, the entire brain will entrain itself to a frequency of 100 – 60 = 40Hz.
This can also be done with audio by putting a different frequency in each ear. This is called “binaural beats” and the same effect as the method above will happen only with audio. I’ve produced countless soundtracks over the last 10-15 years that entrain the brainwaves into whatever frequency desired.
The problem with all of these methods whether it is the simple flashing lights used at MIT or my differential method that I use is that none of these should be used by anyone who is prone to seizures.
Here is a soundtrack made of pink noise, similar to white noise but smoother, and on each channel, frequencies are embedded in order to stimulate a 40Hz gamma wave in the entire brain. This soundtrack was produced in a WAV format and is very high resolution. It was put into a WMV video to make it easy to access on YouTube.
It is 90 minutes long – the first 15 minutes ramps the brainwaves slowly from 12Hz to 40Hz. The next full 60 minutes maintains the brainwaves at 40Hz and then final 15 minutes slowly slides the brainwaves from 40Hz down to 12Hz.
SHORTER BRIEF VERSION BELOW THE 90 MINUTE VIDEO
NO MEDICAL CLAIMS ARE GIVEN FOR THIS AUDIO – THIS IS JUST AN AUDIO EXPERIMENT – DO NOT USE THIS IF YOU ARE PRONE TO SEIZURES – DO NOT DRIVE OR OPERATE HEAVY MACHINERY FOR AT LEAST 60 MINUTES AFTER USING THIS AUDIO – THIS MUST BE USED WITH HEADPHONES OR IT WILL NOT WORK!
YOU MUST USE THIS SOUNDTRACK WITH HEADPHONES
It is 30 minutes long – the first 10 minutes ramps the brainwaves slowly from 12Hz to 40Hz. The next full 10 minutes maintains the brainwaves at 40Hz and then final 10 minutes slowly slides the brainwaves from 40Hz down to 12Hz.
If you want to try to download these YouTube videos or just the audio, check out some links on Google: https://www.google.com/search?q=how+to+download+youtube+video we can’t provide help with this because there are too many computer setups, browser types, etc… but its usually done with a simple browser plugin.
FULL ARTICLE: http://news.mit.edu/2016/visual-stimulation-treatment-alzheimer-1207